Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan, also referred to as a sonogram, diagnostic sonography, and ultrasonography, is a technique that uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of some part of the inside of the body, such as the liver, kidneys, stones, heart, tendons & muscles and blood vessels. Ultrasound scans are absolutely safe and hence very popular in Obstetric Sonography, used to check the well being of the baby in the womb.
Ultrasound scans are used to detect problems in the liver, heart, kidney or the abdomen. They may also be useful in helping the surgeon when carrying out some types of biopsies.
In diagnostic sonography, the ultrasound frequency is usually between 2 and 18 MHz. Higher frequencies provide better quality images, but are more readily absorbed by the tissues, so they cannot penetrate as deeply as lower frequencies. Lower frequencies can penetrate deeper, but the image quality is not as high. Frequencies are selected depending on the type of patient and the part under examination.
IS ULTRASOUND SAFE?
Ultrasound scans have been used in pregnancy for decades, and nobody has ever found them to be harmful. But to be on the safer side, there are clear guidelines on the use of scans in pregnancy. Studies have found no link between ultrasound and birth weight concerns, childhood cancers, dyslexia or hearing impairment.
IS ULTRASOUND USED FOR TREATMENT ALSO?
According to Medilexicon’s medical dictionary:
“The use of ultrasound to obtain images for medical diagnostic purposes, employing frequencies ranging from 2.0 to about 18 MHz.”
“High intensity ultrasound causing coagulation necrosis of tissue, used in treatment of some benign tumors, such as uterine leiomyomata.” Thus, a certain type of ultrasound energy is also used for treatment of some diseases.
WHAT IS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AN ULTRASOUND SCAN AND A SONOGRAM?
Ultrasound scans have been used in pregnancy for decades, and nobody has ever found them to be harmful. But to be on the safer side, there are clear guidelines on the use of scans in pregnancy. Studies have found no link between ultrasound and birth weight concerns, childhood cancers, dyslexia or hearing impairment.
An ultrasound scan is the procedure, the event
A sonogram is the image produced when an ultrasound scan is performed
HOW DOES ULTRASONOGRAPHY WORK?
Although ultrasound travels through soft tissue and fluids, it is reflected back from change of tissue densities. Ultrasound will travel through blood, for example in the heart chamber, but much of it will echo (Reflected) when hitting a heart valve.
If there are no solid gallstones in the gallbladder, ultrasound will travel straight through, but when there are solid stones, ultrasound will reflect back from there surfaces to create an image.
The denser the object the ultrasound hits, the more of it is reflected back.
The reflected back, or echo, is what gives the ultrasound image its features – varying shades of gray reflect different densities.
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SCANS BE USED FOR?
Ultrasound is very commonly used in the practice of medicine today. Health care professionals can use sonography for either diagnosis or treatment (Therapeutic procedures), as well as for guidance during procedures that require intervention, such as biopsies.
Below are examples of medical sonography:
Cardiology -
Used in echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound. Two-dimensional slices of the heart are imaged. Modern devices can produce 3-dimensional images. As well as creating images of the cardiovascular system, echocardiograms can accurately assess the speed of blood flow and cardiac tissue at specific points using pulses or continuous wave Doppler ultrasound. Arterial sonography can also be used to assess the patency and possible blockage of arteries, as well as diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Venosonography may help determine how severe a case of venous insufficiency might be.
Emergency Medicine –
The use of ultrasound in emergency medicine has grown considerably over the last two decades. In emergency medicine, ultrasound is used in the FAST, pericardial tamponade, haemoperitoneum and problems related to blood vessels and many more. Sonography is also used to speed up care for patients with suspected gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder. These patients usually come in with abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant.
Abdominal Sonography (Gastroenterology) –
The healthcare professional is able to see images of the spleen, kidneys, bile ducts, gall bladder, liver, aorta, inferior vena cava, pancreas and other solid organs located in the abdomen.
Newborn Infants (Neonatology) -
The Sonographer can perform an ultrasound scan on an infant by placing the probe in the newborn’s fontanelle (Soft spot in the skull) to check for abnormalities in the brain.
Neurology -
Ultrasound may be used to measure blood flow in the carotid arteries.
Obstetric Ultrasonography -
Ultrasound is used to create images of the fetus or embryo in the uterus. Obstetric Ultrasonography can reveal various aspects of the health of the baby, as well as the health of pregnant mother. It can also help the health care professional assess the progress of the pregnancy. A Doppler Sonography shows the fetus’ heartbeat, and can help the doctor detect signs of abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels.
Urology -
Organs in the pelvic region are checked, including the kidneys and ureters, testicles (To tell testicular torsion from epididymitis). In young adult male patients, ultrasound is sometimes used to distinguish hydrocele or varicocele from testicular cancer.
Musculoskeletal Sonography -
This can be used to examine ligaments, bone surfaces, soft tissue masses, nerves, muscles and tendons.
WHY IS BREAST ULTRASOUND DONE?
To determine the nature of a Breast abnormality
As supplemental Breast Cancer screening
For ultrasound-guided Breast Biopsy
WHEN ARE PREGNANCY SCANS USUALLY CARRIED OUT?
During your first trimester you may have an early scan at about six weeks or seven weeks. But this will only be if you are experiencing problems, such as pain or vaginal bleeding.
Your first scan is likely to be a dating scan when you are between 10 weeks and 13 weeks plus six days pregnant. This will confirm your due date.
The dating scan is important if you are having screening tests for Down’s syndrome, as a correct due date is needed to make the result accurate. You can have a nuchal translucency (NT) scan at 11 weeks and 13 weeks plus six days of your pregnancy, or when your baby measures between 45mm and 84mm. This will, in most cases, be combined with a blood test for increased accuracy.
In your second trimester you should have an anomaly scan at about 20 weeks. This is to check that your baby is developing normally. Now a days, Level 2 ultrasound scans are performed for minute details of the foetal structure to rule out any possible abnormalities.
Level-2 scans are getting more popular as the families are getting smaller and each pregnancy is becoming a precious event in the family.
In your third trimester, you may be recommended to have a growth scan between 28 weeks and 40 weeks. This will be if you:
Previously gave birth to a small baby
Are having twins
Have other complications, such as diabetes
Are pregnant with a baby who measures smaller than expected
WHAT IS DOPPLER ULTRASOUND?
Color Doppler -
The blood flow’s average velocity is estimated via a system of color coding the data. Blood flow direction is assigned the color blue or red, one color indicates whether blood is moving towards and the other away from the ultrasound transducer.
Pulse Doppler -
This method allows the health care professional to see a full range of blood velocities within a sampling volume (Gate). In this method, shades of gray determine how many red blood cells there are.
Power Doppler –
The power of Doppler signals is depicted, instead of the frequency shift. Small vessels can be better visualized, at the expense of blood velocity and directional data.
Put simply, Doppler ultrasound is used to determine how well blood is flowing in a vessel – this includes determining blood velocity and whether there are any obstructions, and how badly they affect blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound can be used to check the heart and heart beat of the foetus.
Color flow ultrasonography (Doppler) of a carotid artery – scanner and screen
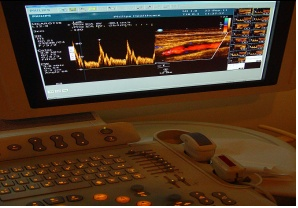
SCAN
Doppler ultrasound – Images of fetal heart (heart beat)
PREPARING FOR AN ULTRASOUND
WHAT IS DOPPLER ULTRASOUND?
In most cases, no special preparation is needed before going for a routine ultrasound scan except filling the urinary bladder with urine for abdominal and pelvic scan. Experts advise patients to wear loose-fitting and comfortable clothing.
If the doctor wants to check your liver or gallbladder, you will be usually asked to eat nothing (Fast) for several hours before the procedure.
If you are going for a scan during pregnancy, especially early pregnancy, the doctor or nurse will ask you to drink several glasses of water and not go to the toilet (No pass urine) for several hours before the test. When the bladder is full the nearby loops of the intestine are displaced, and the scan produces a better image of the uterus.
The majority of scans take between 10 to 30 minutes and will usually occur in the Radiology department in a Diagnostic Center.
Color Doppler
A Doppler ultrasound test uses reflected sound waves to evaluate blood as it flows through a blood vessel. It helps doctors evaluate blood flow through the major arteries and veins of the arms, legs, and neck. It can show blocked or reduced blood flow through narrowing in the major arteries of the neck that could cause a stroke. It also can reveal blood clots in leg veins (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT) that could break loose and block blood flow to the lungs (pulmonary embolism). During Doppler ultrasound, a handheld instrument (transducer) is passed lightly over the skin above a blood vessel. The transducer sends and receives sound waves that are amplified through a microphone.

The sound waves bounce off solid objects, including blood cells. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves (called the Doppler effect). If there is no blood flow, the pitch does not change. Information from the reflected sound waves can be processed by a computer to provide graphs or pictures that represent the flow of blood through the blood vessels. These graphs or pictures can be saved for future review or evaluation. See an illustration of a Doppler ultrasound.

Some of the uses of Color Doppler are:
- Obstetric color Doppler with Bio-Physical Profile
- Testis
- Limbs
- Testis
- Abdomen (Renal)
- Scrotum
- Peripheral Vascular Color Doppler
- Pelvis
- Head
- Carotid
- Penile Doppler




